ESG reporting frameworks
With ESG frameworks and mandatory sustainability disclosures in the EU and beyond, corporate ESG reports and sustainability performance are under more pressure than ever. Investors, customers, employees and regulators all want transparent, verifiable data — and authentic storytelling. Including ESG disclosures and sustainability reports in annual reports provides transparency and accountability around sustainability initiatives and impacts. Companies can publish ESG reports using GRI standards as standalone documents or as part of their annual report to communicate their material ESG impacts. And managing financial risks around ESG issues is key to a holistic sustainability strategy.
That’s where solar displays come in. They allow companies to monitor and report on their environmental impact and live their sustainability values.
What is ESG
ESG (Environmental, Social and Governance) reporting is a key part of corporate sustainability, allowing companies to disclose their environmental, social and governance performance to stakeholders. ESG reporting is essential for businesses to show their commitment to responsible business practices, sustainability initiatives and environmental stewardship, sustainability performance. The Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) are the main ESG reporting frameworks that provide guidance on ESG disclosure. By reporting ESG, companies can improve their reputation, attract investors and contribute to a more sustainable future. Financial risk disclosures within these frameworks, such as those promoted by the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD), are key to revealing the financial implications of ESG factors. These frameworks help companies to align their operations with global sustainability goals, sustainability goals, so their efforts are transparent and accountable. As stakeholders demand more sustainability information, ESG reporting is a tool for companies to show their commitment to a more sustainable future.
What is ESG reporting?
ESG reporting means the disclosure of information about a company’s Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) performance, also known as ESG disclosures. It provides stakeholders with an overview of a company’s sustainability initiatives, environmental impact and social responsibility, sustainability performance. ESG reporting is essential for companies to show their commitment to responsible business practices, manage climate risks and promote sustainable growth, sustainability goals. The Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) are the two main ESG reporting frameworks that provide guidance on ESG reporting. While voluntary disclosures can complement mandatory requirements, they must be consistent with the financial information in the accounts and can take many forms, including sustainability reports or website presentations.
ESG Reporting Requirements
ESG reporting requirements vary by region, with the EU’s Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) being one example. The CSRD requires large public interest entities to report on their sustainability performance, including environmental, social and governance aspects and sustainability performance. In the UK, companies are required to report on their climate-related financial disclosures in line with the recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD). ESG reporting requirements are becoming more widespread, with financial institutions and large companies being subject to more stringent disclosure requirements. The International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB) is also developing global sustainability disclosure standards which will harmonize ESG reporting requirements. These standards will include financial risk disclosures so companies reveal both their impacts and financial implications. These evolving regulations mean companies will provide consistent and reliable ESG data, so stakeholders can make informed decisions and transparency in corporate sustainability and global sustainability goals.
ESG data and disclosure
ESG data and disclosure are key parts of a company’s ESG reporting process. The Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) provide frameworks for companies to disclose their ESG data, including environmental, social and governance (ESG) information. Accurate, reliable and transparent ESG reporting is essential to meet stakeholder expectations and comply with ESG regulations. The Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) and Climate-Related Financial Disclosure (CRFD) regulations require companies to disclose their climate-related financial disclosures and ESG risks. Using ESG reporting software can simplify the reporting process, ensure compliance with ESG reporting requirements and improve the overall reporting process. By following these frameworks and regulations, companies can demonstrate their commitment to corporate sustainability and responsible business practices.
Why ESG Reporting Frameworks Are Changing
In 2025, more companies than ever will be subject to:
- CSRD (Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive)
- EU Taxonomy
- Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR)
Understanding ESG regulations is crucial for companies to increase trust and transparency in their ESG reporting, especially with the EU Taxonomy and Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation guiding sustainability efforts and sustainability performance.
EU regulations and the Companies Act 2006 have significant implications for UK companies, especially post-Brexit. UK companies must navigate new compliance requirements, particularly around sustainability and stakeholder engagement.
These frameworks require businesses to quantify and to communicate their environmental and social performance — particularly in areas like:
- Energy consumption
- Carbon footprint
- Use of renewable energy sources
But how do you turn internal data into a message? That’s where live energy visualisation bridges the gap between technical ESG KPIs and public-facing sustainability communication, increasing transparency and accountability through climate reporting, aligning with global sustainability goals and sustainability goals.
ESG frameworks and regulations
There are many ESG frameworks and regulations to comply with, including the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD), Climate-Related Financial Disclosure (CRFD) and the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD). These frameworks and regulations aim to increase transparency and accountability in ESG reporting and provide stakeholders with accurate ESG data. The EU’s CSRD for example requires large public interest entities to report on their sustainability performance including sustainability performance, environmental, social and governance factors. The European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) mandated by the EU’s Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) require organisations to provide ESG disclosures across various environmental and social topics. In the UK the Streamlined Energy and Carbon Reporting (SECR) framework requires companies to report on their energy use and greenhouse gas emissions to meet global sustainability goals.
Environmental
Environmental is a key part of ESG reporting, focusing on a company’s environmental impact and greenhouse gas emissions. Companies must disclose their carbon emissions and environmental objectives and their strategy to reduce their environmental footprint. The EU Taxonomy provides a framework for companies to disclose their environmentally sustainable activities and climate-related risks. Sustainability reporting frameworks such as the GRI guide companies to disclose their environmental stewardship and sustainability initiatives. By prioritising environmental companies can contribute to a more sustainable future and mitigate financial risks associated with climate change. Effective environmental reporting increases transparency and aligns with global sustainability goals so companies are accountable for their environmental impact.
Corporate Governance and ESG
Corporate governance is key to ESG reporting as it ensures companies are managed in a responsible and transparent way. The UK Corporate Governance Code for example highlights the importance of establishing a corporate culture that promotes integrity, values diversity and is aligned to the company’s purpose and business strategy. Companies must also disclose their corporate governance structure including the composition of their board of directors and executive compensation. Effective corporate governance is essential for managing ESG risks, promoting sustainable practices and long term financial performance. Mandatory climate-related financial disclosures must be included in the strategic report to integrate climate-related information to better analyse risks and opportunities and align with global sustainability goals and sustainability goals.
Governance and Compliance
Governance and compliance are key to ESG reporting, companies must operate in a responsible and transparent way. The UK Corporate Governance Code and EU regulations provide a framework for companies to disclose their corporate governance and ESG compliance. Companies must ensure their board of directors are committed to ESG initiatives and sustainability efforts and have a risk management system in place to identify and mitigate ESG risks. The International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB) provides guidance on sustainability disclosures and ESG reporting frameworks to help companies comply with ESG regulations and stakeholder expectations. By prioritising governance and compliance companies can maintain a strong reputation and contribute to sustainable growth. Effective governance practices not only increase corporate accountability but also long term financial performance and resilience.
Social
Social is a key part of ESG reporting, encompassing a company’s impact on society including its employees, customers and communities. Social metrics include diversity and inclusion, human rights and community engagement. Companies must demonstrate their social commitment through their ESG reporting, highlighting their initiatives and progress in these areas. The UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) provide a framework for companies to align their social initiatives with global sustainability goals and sustainability goals. By prioritising social companies can contribute to a more equitable and just society and enhance their reputation and attract socially responsible investors. Effective social practices not only improve a company’s ESG scores but also a positive corporate culture and stakeholder relationships.
ESG and Corporate Sustainability
ESG reporting is a key part of corporate sustainability as it allows companies to disclose their environmental, social and governance (ESG) performance and progress towards sustainability goals. The Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) is a key regulation that requires companies to report on their sustainability performance including climate-related financial disclosures. By providing stakeholders with ESG data companies can demonstrate their commitment to responsible business practices and contribute to a more sustainable future. Effective ESG reporting frameworks such as the GRI can help companies navigate the reporting process and ensure they are providing high quality, relevant information to stakeholders. These frameworks guide companies to align their operations with global sustainability goals, increase transparency and accountability in their sustainability reporting.
ESG and Stakeholder Engagement
Stakeholder engagement is a key part of ESG reporting as it allows companies to understand the needs and expectations of their stakeholders and report on the issues that matter most to them. Companies can engage with stakeholders through various means including surveys, focus groups and stakeholder meetings to identify the most relevant ESG factors and report on their performance accordingly. By prioritising stakeholder engagement companies can ensure their ESG reporting is relevant, useful and effective in communicating their sustainability efforts and progress. The EU’s sustainability reporting standards such as the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) also highlight the importance of stakeholder engagement in the reporting process. This approach not only improves the quality of the ESG data but also builds trust and credibility with stakeholders.
ESG and Risk Management
ESG reporting is closely linked to risk management as it allows companies to identify, assess and manage ESG risks that could impact their financial performance and reputation. By reporting on climate-related financial risk disclosures companies can provide stakeholders with insight into their exposure to climate-related risks and opportunities and demonstrate their ability to manage those risks. The Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) provides a framework for companies to report on climate-related risks and opportunities and many financial institutions are now requiring companies to disclose this information. Effective ESG reporting can help companies to identify and manage ESG risks and contribute to a more sustainable and resilient business model. This proactive approach to risk management ensures companies are better prepared to navigate the challenges and opportunities presented by climate change and other ESG factors.
ESG and Goal Tracking
ESG reporting is key to tracking progress towards sustainability goals and objectives as it provides a framework for companies to measure and report on their ESG performance over time. By setting clear ESG goals and targets companies can demonstrate their commitment to sustainability and track their progress towards achieving those goals. The Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) provides a framework for companies to report on their sustainability performance including ESG metrics and targets. Effective ESG reporting can help companies to identify areas for improvement, track their progress over time and demonstrate their commitment to sustainable growth and development. The use of ESG scores and ratings can also provide a useful benchmark for companies to track their progress and compare their performance with peers. This continuous monitoring and reporting process ensures companies remain accountable and transparent in their sustainability efforts.
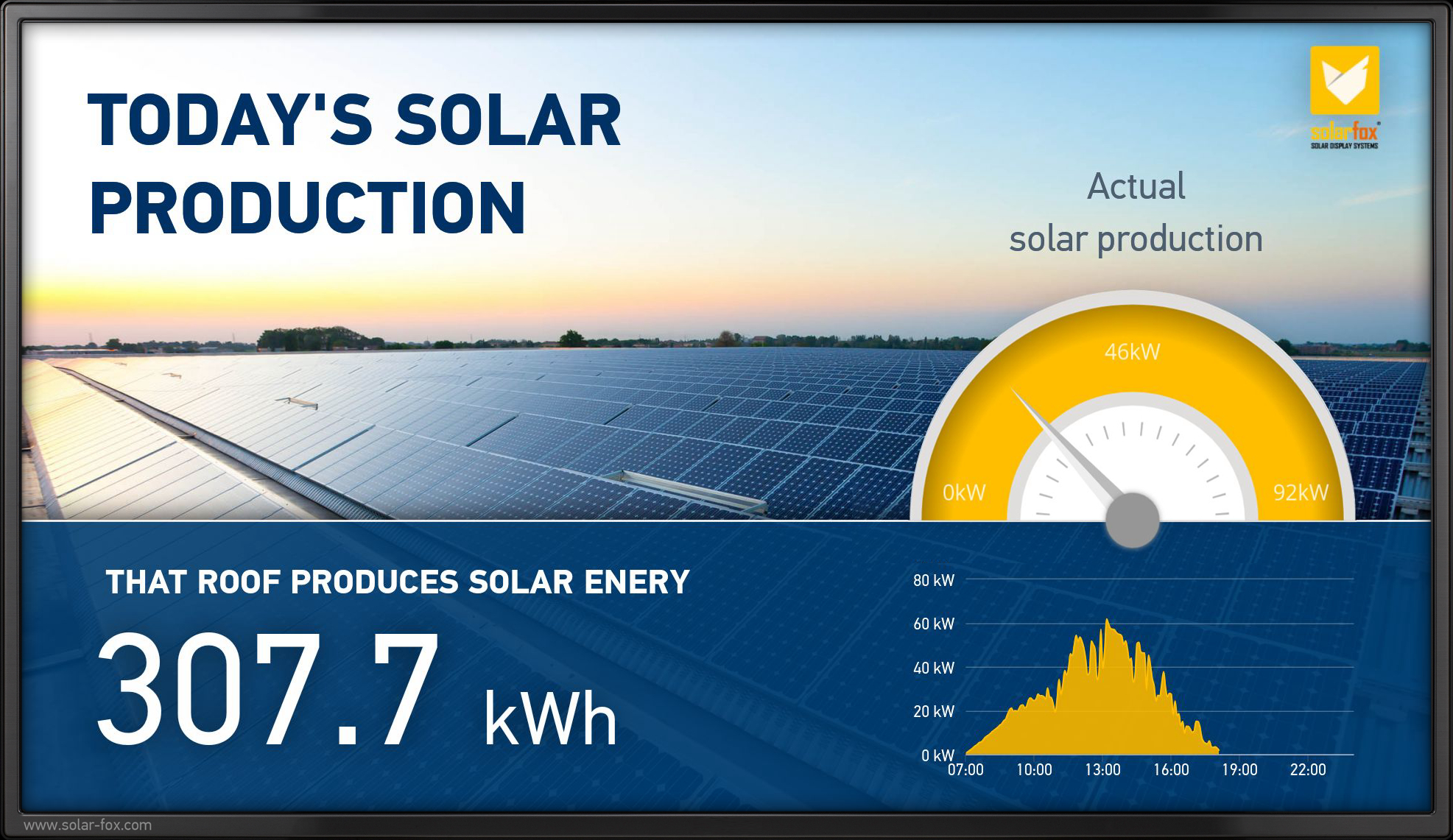
How Solar Displays Improve ESG Reports
Solar power is a goldmine for ESG metrics — if used right. Companies that operate photovoltaic systems can integrate the following live data into their ESG reports:
- Total kWh of solar energy produced
- Percentage of energy demand covered by renewables
- CO₂ savings (yearly, lifetime)
- Self-sufficiency rate (with battery systems)
An esg score reflects a company’s performance on environmental, social and governance aspects and is increasingly important for stakeholders and investors to assess investment risks and opportunities.
By installing solar displays in public areas (e.g. lobbies, cafeterias, reception zones) you make these values visible — for internal stakeholders and visitors. You create transparency, trust and engagement. This helps to promote genuine sustainable practices within companies by adhering to standardized definitions of what is considered environmentally sustainable performance.
These efforts align with global sustainability goals and demonstrate a commitment to achieving sustainability goals.
From Passive Reporting to Active Communication
A solar display does more than show data — it:
- Visualizes progress in real time
- Educates employees and guests
- Promotes the brand as a responsible, future-oriented business
- Provides verified input for ESG reporting tools and platforms
ESG reports are no longer just about ticking boxes — they’re about showcasing a culture of accountability. ESG compliance is key to align business operations with sustainability principles, enhance transparency, accountability and long-term value.
This transition from passive reporting to active communication is further supported by voluntary disclosures which enhance trust and transparency with stakeholders and highlight sustainability performance. These efforts align with global sustainability goals and demonstrate a commitment to continuous improvement.
Case Example: Mid-Sized Manufacturer in Germany
A manufacturing company with a 120 kWp PV system uses a Solarfox® display in its lobby. The screen shows:
- Current and historical solar yield
- Annual CO₂ savings
- A comparison between solar and grid electricity
- A company-specific ESG mission statement
Managing climate-related risks within the context of regulatory frameworks such as the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) and the Prudential Regulation Authority’s supervisory expectations is crucial. Companies must disclose their approaches to governance, strategy and risk management concerning climate risks and opportunities to ensure compliance with new listing rules from the Financial Conduct Authority and relevant investment regulations.
Result:* Over 100 daily visitors can see ESG values and sustainability performance
- Data is referenced in investor meetings and stakeholder reports
- Employee engagement with sustainability has increased and financial institutions consider these sustainability standards when making investment decisions to align with global sustainability goals and sustainability goals
Solar Displays for ESG Communications
ESG is key to corporate governance, focusing on risk management, environmental performance and overall corporate governance.
By using solar displays, companies can boost their ESG communications by providing real-time energy and emissions data. This helps them to disclose information transparently and increase accountability and trust among stakeholders. Report highlights from ESG reporting can inform decision-making, e.g. identifying high water usage in production and companies implementing water-saving technologies to meet global sustainability goals.
ESG Reporting Tools
ESG reporting tools are essential for companies to manage their ESG data and disclosure. These tools help companies to collect, analyze and report their ESG data in a consistent and transparent way. ESG reporting tools can help companies to identify and manage their ESG risks, opportunities and metrics, as well as stakeholder engagement and communication. ESG reporting tools can also increase the accuracy and reliability of ESG data, reducing errors and inconsistencies. By using ESG reporting tools companies can simplify their ESG reporting, improve their ESG performance and contribute to a more sustainable future. These tools help companies to meet their reporting requirements and achieve their global sustainability goals and sustainability objectives.
ESG Best Practices
Best practices for ESG reporting are to use recognized ESG reporting frameworks like GRI or SASB and ensure transparency and consistency in ESG disclosure. Companies should engage with stakeholders to understand their ESG expectations and priorities and report on ESG and sustainability performance in a clear and concise way. ESG reporting software and tools can also help to simplify the ESG reporting process, to collect, analyze and report ESG data more efficiently. Companies should also prioritize ESG risk management, identify and address ESG risks and opportunities. By following best practices for ESG reporting companies can enhance their reputation, attract investors and contribute to a more sustainable future. Implementing these practices ensures companies stay compliant with evolving regulations and meet the growing demands of stakeholders for comprehensive and transparent ESG information and global sustainability goals.
ESG Challenges and Future
ESG reporting is evolving fast and companies face several challenges in implementing effective ESG reporting. These challenges are data accuracy, stakeholder management and regulatory complexity. The future of ESG reporting will be shaped by emerging trends like technology to enhance reporting, growing importance of stakeholder engagement and more comprehensive and transparent reporting. Companies must be able to disclose ESG and sustainability performance in a clear and concise way, using standardized ESG metrics and frameworks. The International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB) will play a key role in promoting global consistency in ESG reporting and companies must be prepared to adapt to changing regulatory requirements and stakeholder expectations. Climate-related financial disclosures should cover four areas—governance, strategy, risk management and metrics and targets—to increase transparency and inform investment decisions. These disclosures will help to align corporate actions with global sustainability goals and sustainability goals.
How to Integrate Solar Displays into Your ESG Strategy
Step 1: Identify key ESG metrics related to energy use and CO₂ savings
Organizations must assess labor practices and human rights within their own operations and their supply chain, engage suppliers in promoting environmental stewardship.
Step 2: Connect your PV system to a monitoring tool or API. ESG reporting software is essential to simplify the collection and analysis of ESG data, so organizations can report effectively on environmental, social and governance performance and sustainability performance.
Step 3: Install a solar display in a public areaStep 4: Include screenshots, KPIs and system specs in your ESG report
Step 5: Communicate internally and externally (e.g. via LinkedIn, newsletters, press releases) to build trust and credibility not only with investors and customers but also with other stakeholders. Highlight how your efforts align with global sustainability goals and sustainability goals.
Smart Use of Technology to Build ESG Trust through Climate Related Financial Disclosures
In an era where greenwashing is under fire, authenticity and transparency are key. A solar display is a simple yet powerful tool to support your ESG narrative. Corporate governance data is essential to transparently communicate your sustainability efforts and responsible business practices to stakeholders, enhance your sustainability performance.
And unlike long reports that are read once a year, a display shows your impact every day — to employees, partners and clients. Integrating risk management into corporate strategies and disclosures, especially climate-related risks and opportunities, is vital for compliance with guidelines like TCFD. CSRD will require comprehensive sustainability related information beyond climate aspects, focusing on a double materiality approach to meet global sustainability goals.
FAQs
Are solar displays compatible with all PV systems? Most modern displays (e.g. Solarfox) work with over 30+ PV monitoring platforms and can be installed in a few hours.
Is this relevant for small businesses too? Absolutely. Transparency builds trust — and even small systems can be used to show measurable impact.
Can the display data be reused in ESG software? Yes. The same data feed can be exported for reporting platforms or used in PDF reports and presentations.
Why are climate-related disclosures important in ESG reporting? Climate-related disclosures, like those introduced by the ISSB’s sustainability standards (IFRS S1 and IFRS S2), are crucial for businesses and financial institutions. They help in reporting, resilience to regulatory changes and informed decision-making, to ensure companies are transparent about their climate impact and sustainability performance. While ESG-related documents like modern slavery statements and gender pay gap reports are important, they don’t need to be included within the financial statements of a business.How does the framework affect ESG reporting? Choosing the right ESG reporting framework is key for publicly traded companies to communicate their sustainability and performance metrics. It ensures compliance with local requirements and highlights the materiality and impact of their ESG efforts towards global sustainability goals.
Turn Data Into a Story
Your ESG report shouldn’t be a hidden PDF. It should be a story your employees and partners can experience. A well-defined sustainability strategy within these reports helps companies to demonstrate accountability and transparency to stakeholders and guide leaders to make changes for a sustainable future. Mandatory disclosures like climate risk assessments and social issues are required by legislation and regulations and are critical for transparency and compliance.
A solar display turns your sustainability performance into a story — and gives your ESG values a physical presence. Because sometimes the most powerful way to say “We care” is to show it. Including ESG in your reporting requirements and frameworks ensures your organization assesses the materiality and impact of these factors and improves your reporting and aligns with global sustainability goals.